
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
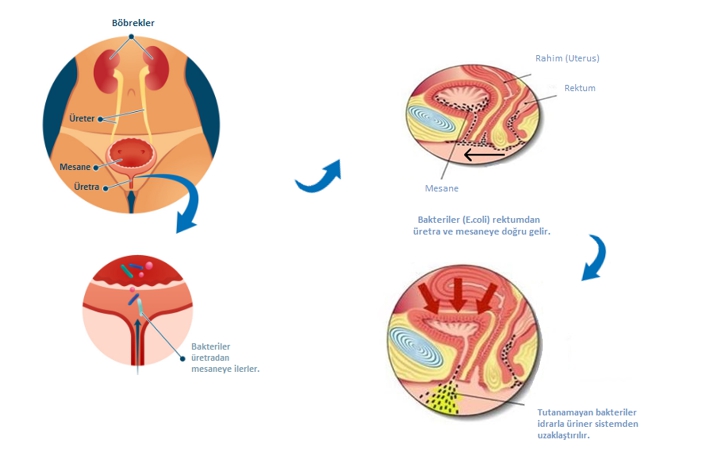
Under normal conditions, there are no microorganisms in the urinary (excretory) system. Intestinal bacteria (enteric bacteria), upon contact with the urethra (the canal through which urine is discharged), adhere to this area and multiply, causing infection. From this region, they proceed to the bladder, causing bladder inflammation (cystitis). If the infection is not treated, it can spread to the urinary system, causing more serious problems.
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is more common in women than in men. The main reason for this is that the urethra is shorter in women than in men. Not properly maintaining genital hygiene, the use of hygiene products that disrupt the genital flora increases the risk, while the likelihood of UTI is higher in women who are sexually active and in menopause
It also frequently affects young and sexually active women. Urinary tract infections are usually caused by bacteria known as E. Coli and its types. These bacteria have special extensions. With these extensions, the bacteria can adhere to the related place. Attachment/adhesion constitutes the first step in the formation of an infection.
The main symptoms of a Urinary Tract Infection are;
Burning and pain while urinating (Dysuria), Increased frequency of urination, Cloudy urine and sometimes blood can be seen in urine (hematuria).
UTI symptoms can have significant impacts on a person's quality of life. Although antibiotics are often preferred for recurrent UTI treatment to control these infections, prescribing antibiotics without identifying the causative bacteria and irrational use of antibiotics significantly contribute to antibiotic resistance developed in bacteria.
The Relationship between Urinary Tract Infection and Sistinon
Sistinon is a supplemental food that can be used to alleviate symptoms in urinary tract infection, prophylactically for urinary tract infection, and for urinary tract infections seen after catheterization (catheter etc.) procedures. It contains Quercetin, a very powerful natural anti-inflammatory (inflammation-suppressive) that acts in a different way in urinary tract infections, not just with its Cranberry content.
Sistinon Components:
Cranberry: Cranberries have been traditionally used frequently in urinary tract infections for many years. Its fruits contain high amounts of vitamin C. It has the potential to prevent bacteria from adhering to the urinary mucosa.
Proanthocyanidin (PAC): What matters is the amount of a component called proanthocyanidin (PAC) found in Cranberry. Studies have indicated the daily intake should be at least 72 mg.
D-mannose: D-mannose, a sugar component, is another agent aiming to prevent bacteria from causing infection.
Quercetin: : It is a plant-based content found in many different fruits and vegetables, especially shown to have anti-inflammatory effects in clinical studies.
Vitamin C: Vitamin C, known for its antioxidant feature, attracts attention with its antibacterial efficacy and ensures the preservation of cranberries is not affected by storage conditions.
The recommended daily use of Sistinon is 1-2 tablets with meals.
Sistinon Components:
| Components | Amount (1 Tablets) | Amount (2 Tablets) |
| D-mannose | 250 mg | 500 mg |
| Quercetin | 60 mg (76 mg) | 120 mg |
| Vitamin C | 12 mg | 24 mg |



